 |
 |
- Search
| Korean J Fam Med > Volume 34(2); 2013 > Article |
Abstract
Background
The purpose of this study was to examine the association of metabolic syndrome (MS) coronary heart disease (CHD) with socioeconomic status (SES).
Methods
The participants were 2,170 (631 men and 1,539 women), aged over 40 years who had visited for health screening from April to December in 2009. We classified them into three SES levels according to their education and income levels. MS was defined using the criteria of modified National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III and CHD risk was defined using Framingham risk score (FRS) ≥ 10%.
Results
High, middle, and low SES were 12.0%, 73.7%, and 14.3%, respectively. The prevalence of MS was 18.1%. For high, middle, and low SES, after adjusted covariates (age, drinking, smoking, and exercise), odds ratios for MS in men were 1.0, 1.41 (confidence interval [CI], 0.83 to 2.38; P > 0.05), and 1.50 (CI, 0.69 to 3.27; P > 0.05), respectively and in women were 1.0, 1.74 (CI, 1.05 to 3.18; P < 0.05), and 2.81 (CI, 1.46 to 2.43; P < 0.05), respectively. The prevalence of FRS ≥ 10% was 33.5% (adjusted covariates were drinking, smoking, and exercise) and odds ratios for FRS ≥ 10% in men were 1.0, 2.86 (CI, 1.35 to 6.08; P < 0.001), and 3.12 (CI, 1.94 to 5.00; P < 0.001), respectively and in women were 1.0, 3.24 (CI, 1.71 to 6.12; P < 0.001), and 8.80 (CI, 4.50 to 17.23; P < 0.001), respectively.
It has been widely reported that lower socioeconomic status (SES) was associated with higher risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).1,2) The indicators of SES measurements3) including level of education, income, and occupation, were known to be associated with health status including mortality, CVD, diabetes, and health behaviors.4) In Korea, the 'Establish a New Health Plan 2010' project, published in 2005, aimed to achieve prolongation of healthy life span and health equity. The project also targeted reducing the gap in health status among different classes of SES.5) The report conducted by the Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs (KIHASA) found that there were differences in mortality and health behaviors according to SES, especially when the lowest 20% were compared with the highest 20%.4)
Some studies also showed that SES and health level were reciprocally related. Levels of SES could influence the level of health because they determine the accessibility and usability of health resources. Vice versa, the level of health could influence the level of SES because they could affect educational achievement and choice of occupation unfavorably.6-8)
In this study, we utilized education and income as indicators of SES, and metabolic syndrome (MS) and Framingham risk score (FRS) ≥ 10%, which are commonly used to evaluate risk of CVD. MS is simple, easily applied, and more predictable for type II diabetes, whereas FRS ≥ 10% is known more specifically for men.9)
MS includes central obesity, dyslipidemia, high blood pressure (BP), and insulin resistance.10-12) Recent epidemiologic studies reported that lower SES correlated with a higher prevalence of MS. The 'Whitehall II study' a prospective study over 15 years reported that lower SES increased the incidence of MS 3 to 5 times, in both men and women.13) FRS ≥ 10%, including age, total cholesterol, smoking, high density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol, and systolic blood pressure (SBP) were known to evaluate the risk of CVD incidence within 10 years. A prospective study showed that higher SES reduced the risks of FRS ≥ 10% and FRS ≥ 20% by 6% and 13%, respectively.14) In the Framingham cohort, lower SES was reported to increase the risk of CVD by 1.82 (adjusted 1.29) times.15)
The association between SES and health quality have been widely studied in western countries.16) However, in Korea, such studies have been limited,17-20) especially in clinical fields with SES utilized as a covariant variable.21-23) The present study was conducted utilizing SES as an independent variable to investigate the association between SES and CVD risk.
The study population participated in the 'health checkup program of the National Health Insurance Corporation' of Daegu Catholic University Hospital, from April to December, 2009. Health interview was performed by a trained interviewer using a well-established questionnaire to determine SES and health behaviors (smoking, drinking, and physical activity). We analyzed 2,180 persons (636 for men and 1,546 for women) among 2,286 participants, and 116 persons were excluded (inadequate response 83 persons and deleted data 33 persons).
We interviewed demographic factors including age, education, and personal disease history. Life style factors included smoking, drinking, and regular exercise. Smoking status was classified as a "smoker" (including current smoker and past smoker) when the amount of whole-life smoking included over 100 cigarettes. When the drinking frequency of the study population was more than 1 time per 1 month, the participant was classified as a drinker. Also, exercise was categorized as "regular" when the frequency of moderate and vigorous exercise was more than 2 to 3 times per week.
Anthropometric measurements included height, weight, and waist circumference. Height and weight were measured with the subject standing barefoot in light clothes (body mass index, BMI [kg/m2]). Waist circumference was measured at the midpoint between the 12th rib and right anterior iliac spine. BP was measured using an automatic sphygmomanometer on the right arm in sitting position after 5 minutes resting, and average value of SBP and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) was acquired after repeated measurement. Blood samples were collected after overnight fasting to measure fasting blood sugar, triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Referencing KIHASA reports,4) we classified SES into 2-dimensions. The first was education (<12, 12-15, and >15 years) and the other was house income (<1,000,000, 1,000,000-3,000,000, and >3,000,000 won). We divided into 3 groups: the higher SES belongs to highest education and house-income and the lower SES belongs to lowest education and house-income. The others were middle SES. The proportion of higher, middle, and lower SES was 12.0%, 73.7%, and 14.3%, respectively.
MS was defined according to the modified National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel-III (NCEP-ATP III).24) Subjects with three or more of the following criteria were classified as having MS: 1) waist circumference ≥ 90 cm in men or ≥ 80 cm in women, 2) TG ≥ 150 mg/dL or medication, 3) HDL-cholesterol < 40 mg/dL in men or in women < 50 mg/dL in women or medication, 4) BP ≥ 130 mm Hg systolic or ≥ 85 mm Hg diastolic or medication, and 5) fasting blood sugar ≥ 110 mg/dL or medication.
We used Framingham risk scoring to derive the 10-year risk (FRS ≥ 10%) of CVD. FRS ≥ 10% included age, sex, total cholesterol, smoking status, SBP, use of hypertensive agents, family history of premature coronary heart disease, and coronary heart disease equivalents (stroke and diabetes).25) According to the 'Framingham risk scoring model' participants were divided into higher CVD risk (FRS ≥ 10%) and lower CVD risk (FRS < 10%) groups.
Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and significance was designated as P < 0.05. General characteristics were evaluated by SES and gender using a chi-square test, analysis of variance, and t-test. The relationship between SES and health behaviors was analyzed through logistic regression, with age, smoking, drinking, and exercise as covariates. We performed logistic regressions to investigate the association between SES and MS (covariates were age, drinking, smoking, and exercise), and SES and FRS ≥ 10% (covariates were drinking, smoking, and exercise).
Among the study population, the proportion of higher, middle, and lower SES persons was 12.0% (259 persons), 73.7% (1,610 persons), and 14.3% (311 persons), respectively. The levels of SES were inversely related with age, and male participants were older and smoked and drank more heavily than female participants (P < 0.001). For men, the SES level was inversely related with drinking and non-regular exercise, but not smoking, for women however, non-regular exercise was inversely related with SES level. In both men and women, SES level were inversely related with SBP and DBP. In women, waist, HDL-cholesterol, triglyceride, and BMI were inversely related with SES level, but not significantly in men. Regarding disease history for men, SES levels were inversely related with prevalence of hypertension. For women, SES level were inversely related with prevalence of hypertension and diabetes.
The prevalence of MS was inversely associated with SES level, both men and women. For men, the prevalence of MS by SES level was 21.2% in higher SES, 31.6% in middle SES, and 40.6% in lower SES, and was 8.2% in higher SES, 19.4% in middle SES, and 38.5% in lower SES for women. Specifically, in lower SES, gender difference in the prevalence of MS disappeared. It has been shown that the prevalence of FRS ≥ 10% was inversely associated with SES level. For men, the prevalence of FRS ≥ 10% by SES level was 43.3% in higher SES, 65.7% in middle SES, and 67.3% in lower SES, and 7.1% in higher SES, 19.4% in middle SES, and 40.6% in lower SES for women. Gender difference in the prevalence of FRS ≥ 10% was thus constant in each SES level (Table 1).
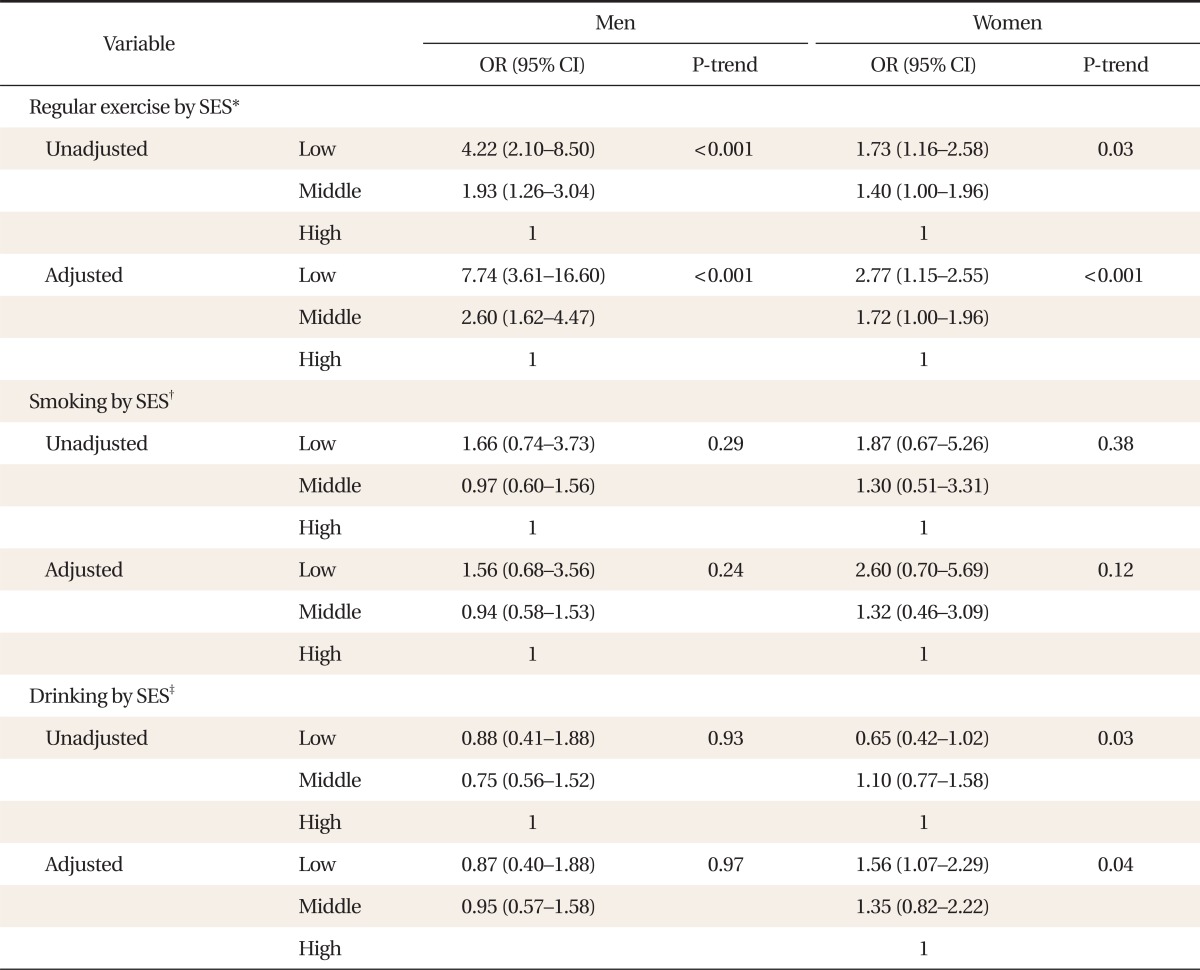
We analyzed the association between SES and health behaviors. After covariates (age, regular exercise, drinking, and smoking) were modified for men, the odds ratios (ORs) of non-regular exercise decreased with SES level as follows: 7.74 (confidence interval [CI], 3.61 to 16.60) in lower SES, 2.6 (CI, 1.62 to 4.47) in middle SES, and 1.0 in higher SES. In women, ORs were 2.77 (CI, 1.15 to 2.55) in lower SES, 1.72 (CI, 1.00 to 1.96) in middle SES, and 1.0 in higher SES. The ORs for drinking also decreased with SES level as follows: 1.56 (CI, 1.07 to 2.29) in lower SES, 1.35 (CI, 0.82 to 2.22) in middle SES, and 1.0 in higher SES, but were not significant for men (Table 2).
There were gender differences among SES level: in men, the proportion of higher SES was 16.2%, middle SES was 75.3%, and lower SES was 8.5%, while in women the proportion was 10.9%, 73.4%, and 16.7%, respectively.
Table 3 shows the ORs for the association between SES and MS in men and women using a logistic model. Model I shows estimates of the association between SES level and MS without adjustment. For men, ORs for MS according to SES level were 1.0 in higher SES, 1.90 (CI, 1.31 to 2.80) in middle SES, and 3.98 (CI, 2.62 to 6.06) in lower SES. In women, the ORs were 1.0 in higher SES, 2.68 (CI, 1.49 to 4.81) in middle SES, and 6.97 (CI, 3.75 to 12.96) in lower SES. Model II was been adjusted for covariates (age, smoking, drinking, and exercise). For men, the ORs were 1.0 in higher SES, 1.41 (CI, 0.83 to 2.38) in middle SES, and 1.50 (CI, 0.69 to 3.27) in lower SES. In women, ORs were 2.81 (CI, 1.46 to 5.43) in lower SES, 1.74 (CI, 0.95 to 3.18) in middle SES, and 1.0 in higher SES.
For men, ORs for the association between SES level and FRS ≥ 10% were 1.0 in higher SES, 2.52 (CI, 1.63 to 3.88) in middle SES, and 2.70 (CI, 1.36 to 5.34) in lower SES without adjustment (model I). After adjustment of covariates (smoking, drinking, and exercise), the ORs for FRS ≥ 10% were 1.0 in higher SES, 2.86 (CI, 1.35 to 6.08) in middle SES, and 3.12 (CI, 1.94 to 5.00 in lower SES (model II). For women, the ORs for FRS ≥ 10% were 1.0 in higher SES, 3.13 (CI, 1.66 to 5.88) in middle SES, and 8.87 (CI, 4.57 to 17.20 in lower SES without adjustment (model I). After adjustment of covariates, ORs (CI) for FRS ≥ 10% were 1.0 in higher SES, 3.24 (CI, 1.71 to 6.12) in middle SES, and 8.80 (CI, 4.50 to 17.23) in lower SES (model II) (Table 3).
The present study showed a linear, inverse relationship between SES level and CVD risks such as MS and FRS ≥ 10%. Lower SES increased the risk of CVD. For men, the relationship between MS and SES was not significant although the OR for MS was increased. In women, however, there was a significant inverse relationship between MS and SES.
For men and women, FRS ≥ 10% was inversely related with SES and the inverse relationship was much stronger for women than men. This result could be interpreted as poor SES conditions impacting women more strongly than men. It was similar to studies of chronic diseases in England and Sweden which reported ORs of CVD in social class V compared with class I as 2.65 in England and 1.5 in Sweden.26)
Health behaviors have been reported to be associated with SES in many studies. In these studies, the ORs of poor health behaviors increased for lower SES groups: for example, lower SES groups showed a tendency to smoke and to exercise less regularly. In contrast, the relationship was reported insignificant in domestic studies.17,18) SES affected health behaviors directly.18) Poor health behaviors such as diet, smoking, leisure time, and heavy drinking, could be well explained by lower social class, showing direct dependence on economic, material, and psychosocial conditions.27)
In this study, the relationship between SES and MS was significant only in women, which was consistent with other studies. Many other studies also showed that lower levels of education had increased the ORs of MS for women, but not for men.19,28,29) House income was reported as inversely related with the prevalence of type II diabetes in women.30) Further domestic studies also reported lower SES increased MS in women but not in men.21)
This study showed FRS ≥ 10% was associated with SES both in women and men and FRS ≥ 10% was more sensitive than MS as a surrogate indicator of CVD risk, especially in men. This may be explained by the fact that FRS ≥ 10% accounts for age, disease history of CVD, total cholesterol, and smoking, while MS does not. Male participants in this study were older and had higher rates of smoking, myocardial infarction, and stroke incidence than female participants. The association between SES and the risk of CVD may be explained through health behaviors, obesity, and stress of social position.30) Wardle et al.29) explained economic deprivation partly intermediated the reciprocal association between SES and health behaviors through 'health related selection theory' and 'social causation hypothesis.'
According to various studies, the relationship between SES and MS could be explained in the following ways: in animal models, the response of the neuroendocrine system resulted in hyper-excitation of the sympathetic system, hyper-secretion of cortisol, and an increase in visceral fat. These changes in endocrine status and distribution in adipose tissue were consistent with the findings of MS.31) In another study, subordinate rats with elevated levels plasma insulin and leptin displayed overeating behavior.31,32)
This study has some limitations. First, the study population was restricted to one university hospital, making it difficult to generalize. Second, we were unable to determine a causal relationship between SES and CVD risks because this study was designed as a cross-sectional study. Third, we could not avoid information bias because this study was based on a questionnaire. Forth, the ambiguities of health behaviors make it difficult to classify which may attenuate the difference in CVD risks by SES. Finally, the validity of FRS ≥ 10% was not determined in Korean.
Despite these limitations, this study included comprehensive variables such as disease histories, health behaviors, education, and house income, and classified SES according to education and income. This study was significant because it enabled us to draw inference on the association between SES and CVD risks.
References
1. Mackenbach JP, Stirbu I, Roskam AJ, Schaap MM, Menvielle G, Leinsalu M, et al. Socioeconomic inequalities in health in 22 European countries. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2468-2481. PMID: 18525043.


2. Kumari M, Head J, Marmot M. Prospective study of social and other risk factors for incidence of type 2 diabetes in the Whitehall II study. Arch Intern Med 2004;164:1873-1880. PMID: 15451762.


3. Wilkinson RG, Pickett KE. The problems of relative deprivation: why some societies do better than others. Soc Sci Med 2007;65:1965-1978. PMID: 17618718.


4. The Korean Society for Equity in Health. Methods in health inequalities measurement. 2008. Paju: Hanul Publishing Co..
5. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. Establish of new health plan 2010. 2006. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs.
6. Chandola T, Brunner E, Marmot M. Chronic stress at work and the metabolic syndrome: prospective study. BMJ 2006;332:521-525. PMID: 16428252.



7. Chandola T, Bartley M, Sacker A, Jenkinson C, Marmot M. Health selection in the Whitehall II study, UK. Soc Sci Med 2003;56:2059-2072. PMID: 12697197.


8. Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Lennon L, Morris RW. Metabolic syndrome vs Framingham Risk Score for prediction of coronary heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 2005;165:2644-2650. PMID: 16344423.


9. Najarian RM, Sullivan LM, Kannel WB, Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Wolf PA. Metabolic syndrome compared with type 2 diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Offspring Study. Arch Intern Med 2006;166:106-111. PMID: 16401818.


10. Karam JH. Type II diabetes and syndrome X: pathogenesis and glycemic management. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1992;21:329-350. PMID: 1612069.


11. Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, Forsen B, Lahti K, Nissen M, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2001;24:683-689. PMID: 11315831.


12. Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, et al. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA 2002;288:2709-2716. PMID: 12460094.


13. De Vogli R, Brunner E, Marmot MG. Unfairness and the social gradient of metabolic syndrome in the Whitehall II Study. J Psychosom Res 2007;63:413-419. PMID: 17905050.


14. Franks P, Tancredi DJ, Winters P, Fiscella K. Including socioeconomic status in coronary heart disease risk estimation. Ann Fam Med 2010;8:447-453. PMID: 20843887.



15. Loucks EB, Lynch JW, Pilote L, Fuhrer R, Almeida ND, Richard H, et al. Life-course socioeconomic position and incidence of coronary heart disease: the Framingham Offspring Study. Am J Epidemiol 2009;169:829-836. PMID: 19179358.



16. Karlamangla AS, Merkin SS, Crimmins EM, Seeman TE. Socioeconomic and ethnic disparities in cardiovascular risk in the United States, 2001-2006. Ann Epidemiol 2010;20:617-628. PMID: 20609342.



17. Kim HR, Kim YS. A study of differences in chronic diseases prevalence between socioeconomic classes. J Korean Soc Health Stat 2003;28:56-66.
18. Son M. The relationship of social class and health behaviors with morbidity in Korea. Korean J Prev Med 2002;35:57-64.
19. Wamala SP, Lynch J, Horsten M, Mittleman MA, Schenck-Gustafsson K, Orth-Gomer K. Education and the metabolic syndrome in women. Diabetes Care 1999;22:1999-2003. PMID: 10587833.


20. Dallongeville J, Cottel D, Ferrieres J, Arveiler D, Bingham A, Ruidavets JB, et al. Household income is associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome in a sex-specific manner. Diabetes Care 2005;28:409-415. PMID: 15677801.


21. Park MJ, Yun KE, Lee GE, Cho HJ, Park HS. The relationship between socioeconomic status and metabolic syndrome among Korean adults. Korean J Obes 2006;15:10-17.
22. Park HS, Kim BS. Prevalence and associated factors of metabolic syndrome among adults in primary care. J Korean Soc Study Obes 2003;12:108-123.
23. Choi YH, Jeong JY, Kwak KS, Kang SH, Jang SN, Choi YJ, et al. The prevalence and risk factors of the metabolic syndrome among local residents aged 45 or over in Chuncheon: Hallym Aging Study. J Korean Acad Fam Med 2006;27:190-200.
24. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005;112:2735-2752. PMID: 16157765.


25. Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Levy D, Belanger AM, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB. Prediction of coronary heart disease using risk factor categories. Circulation 1998;97:1837-1847. PMID: 9603539.


26. Vagero D, Lunberg O. Health inequalities in Britain and Sweden. Lancet 1989;2:35-36. PMID: 2567803.


27. Nelson M. Low Income Project Team. Department of Health. Nutrition Task Force. Low income, food, nutrition and health strategies for improvement. 1996. London: Department of Health.
28. Lidfeldt J, Nyberg P, Nerbrand C, Samsioe G, Schersten B, Agardh CD. Socio-demographic and psychosocial factors are associated with features of the metabolic syndrome: the Women's Health in the Lund Area (WHILA) study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2003;5:106-112. PMID: 12630935.


29. Wardle J, Waller J, Jarvis MJ. Sex differences in the association of socioeconomic status with obesity. Am J Public Health 2002;92:1299-1304. PMID: 12144988.



30. Drewnowski A, Specter SE. Poverty and obesity: the role of energy density and energy costs. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79:6-16. PMID: 14684391.


31. Tamashiro KL, Nguyen MM, Sakai RR. Social stress: from rodents to primates. Front Neuroendocrinol 2005;26:27-40. PMID: 15862183.


32. Neitzke U, Harder T, Plagemann A. Intrauterine growth restriction and developmental programming of the metabolic syndrome: a critical appraisal. Microcirculation 2011;18:304-311. PMID: 21418379.


Table 2
OR and 95% CI from logistic regression for the association between SES and risk behaviors according to gender
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles in KJFM
-
Shift Work Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Young Female Korean Workers2017 March;38(2)
Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microalbuminuria in Korean Adults2015 March;36(2)
The Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome and Pulmonary Function2012 March;33(2)







