|
 |
- Search
| Korean J Fam Med > Volume 42(4); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
ŌĆ£Rusty pipe syndromeŌĆØ is a condition that needs to be considered in a primiparous woman who presents with bilateral bloody nipple discharge in the early postpartum period. Its prevalence is low and can occur due to physiological condition that arises primarily in primiparous women with increased alveolar and ductal vascularization associated with the onset of lactation. Here, we report a case of a 29-year-old primigravida who presented with bilateral painless bloody nipple discharge after delivery. Her breast examination showed no signs of infection or structural changes, and breast ultrasound did not reveal any significant observations except for a bilateral simple breast cyst. Six days after the onset of lactation, the bloody nipple discharge ceased and lactation continued on demand.
Discharge of blood-stained maternal milk after delivery is a rare phenomenon, with an estimated prevalence rate of 0.1% [1]. This uncommon phenomenon can elicit anxiety and concern among the mother and the medical staff [2]. Bloody nipple discharge during lactation occurs as a result of several factors such as cracked nipples, mastitis, trauma, or intraductal papilloma [3,4]. However, a rare physiological condition, known as ŌĆ£rusty-pipe syndromeŌĆØ, can cause painless bloody nipple discharge in pregnant and post-partum women [2,3,5]. Rusty pipe syndrome is a breastfeeding condition in which the color of the breast milk looks pink, orange, brown, or rust-colored, similar to dirty water coming out of an old rusty pipe, and hence, the name of the syndrome. The rusty color is usually due to mixing of colostrum, or first breast milk, with a small amount of blood [2]. The rusty-colored milk usually appears during the first few days of breastfeeding. In most cases, the syndrome is spontaneously cured within 3 to 7 days after the onset of lactation [2,5]. In other cases, this condition persists for the first few weeks of lactation, and is eventually resolved spontaneously [6].
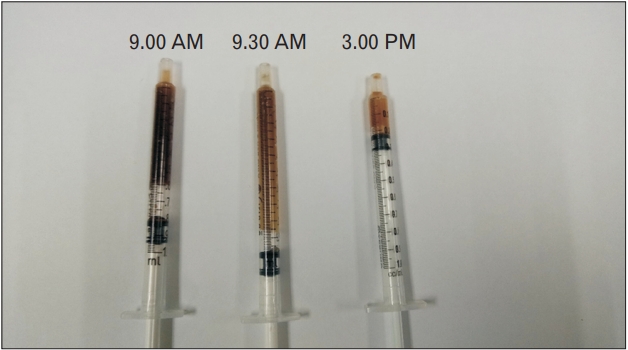
A 29-year-old primigravida delivered a baby boy, with a birth weight of 3,000 g, after 38 weeks of gestation through spontaneous vaginal delivery. She attempted to feed her newborn after delivery; however, the milk did not come out due to the poor attachment technique associated with the bilateral inverted nipple. She was attended by a staff nurse in the ward for inverted nipple using the syringe technique. She noticed bilateral painless bloody nipple discharge while expressing her breast. She observed this phenomenon occurring more on the left breast than on the right breast as shown in Figure 1. She was referred to a lactation unit for further management. The patient denied having any history of trauma to her breast. Her breast examination showed no signs of inflammation, engorgement, tenderness, or palpable masses. The nipples were inverted and showed no cracks, ulcers, or fissures. Examination of the newbornŌĆÖs mouth revealed no natal teeth. She noticed that the nipple discharge color changed from dark brown in the morning to light brown in the afternoon, as shown in Figure 2. She was advised to express her breast every 2 to 3 hours and continue breastfeeding on demand to avoid breast engorgement. A discharge sample was collected for cytological analysis to exclude the presence of malignant cells. Ultrasound of the breasts revealed bilateral simple breast cyst measuring up to 0.5 cm├Ś0.7 cm├Ś0.6 cm on the right and 0.4 cm├Ś0.4 cm├Ś0.7 cm on the left breast. No ductal lesions or enlarged axillary lymph node was observed. The bloody discharge resolved spontaneously 6 days after delivery with the onset of normal milk production, after which, the bloody discharge did not recur.
Informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and accompanying images.
ŌĆ£Rusty pipe syndromeŌĆØ is a rare benign and self-limiting physiological condition that should be included in the differential diagnosis in women who present with painless bloody nipple discharge during gestation and lactation [3]. Rusty pipe syndrome occurs due to elevated vascularization of rapidly developing alveoli that have a delicate network of capillaries. These capillaries are easily traumatized, which results in bleeding from the nipples [3,7]. This condition commonly occurs in primiparous women who present with bilateral painless nipple discharge after delivery, with no signs of inflammation in the breast and no previous history of trauma [3]. The syndrome may begin at the time of birth, during early lactation, or during pregnancy. The onset of the syndrome may involve unilateral breast [4]. It is usually associated with nipple stretching exercises, such as HoffmanŌĆÖs procedure, which is often recommended for flat or inverted nipples [4,5]. However, in our case, the syringe technique was employed to treat the inverted nipple based on the guidelines of ŌĆ£session 12: breast and nipple conditionsŌĆØ by the World Health Organization and United Nations ChildrenŌĆÖs Fund, and Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative, 2009 [8]. In addition, physical examination did not reveal any skin changes, nipple cracks or fissures, breast engorgement or lump, and fever [3].
Initial diagnosis of ŌĆ£rusty pipe syndromeŌĆØ is based on medical history and routine physical examination, followed by specialized investigations, if necessary, including cytological analysis of the bloody discharge, to exclude the presence of malignant cells, and breast ultrasound, which could help rule out other pathological conditions [3,4]. Bloody nipple discharge during lactation can be related to the breastfeeding technique that causes cracked nipples, mastitis, or trauma, and its occurrence can be attributed to various pathological causes such as intraductal papilloma [3,4]. Intraductal papilloma is a benign tumor found within the breast ducts, in which abnormal proliferation of ductal epithelial cells causes tumor growth. A solitary intraductal papilloma is usually found located centrally posterior to the nipple that affects the central duct. Patients often present with spontaneous bloody or clear nipple discharge. An intraductal papilloma may be occasionally palpable. The breast ultrasound usually reveals a mass near the nipple. Tissue sampling, in addition to imaging, is necessary for the diagnosis of intraductal papilloma. Treatment of intraductal papilloma involves surgical excision and complete removal of the tumor [9].
Persistent bloody nipple discharge immediately after the postpartum period should be evaluated using diagnostic imaging. Ultrasonography is recommended as the initial diagnostic imaging modality in a breastfeeding woman. If the ultrasonography reveals suspicious findings or is discordant with the clinical examination, additional imaging using mammography or digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT or ŌĆ£three-dimensional mammographyŌĆØ) may be indicated. This is related to the fact that mammography or DBT can visualize architectural distortion and/or calcifications that cannot be seen on ultrasonography, as well as delineate the extent of the disease in case of malignancy [6].
In summary, ŌĆ£rusty pipe syndromeŌĆØ during pregnancy and lactation is an uncommon and harmless condition, but can be alarming to the mother, caregivers, and medical personnel [10]. It is a self-limiting condition and is usually resolved within three to seven days after onset of lactation [2,5]. In our case, the patient is a healthy primiparous woman who exhibits a typical ŌĆ£rusty pipe syndrome,ŌĆØ with spontaneous and self-resolving bloody nipple discharge. In ŌĆ£rusty pipe syndromeŌĆØ cases, if the infant tolerates the milk, then breastfeeding can be continued and encouraged to strengthen exclusive breastfeeding practice for 6 months [7,10]. The discharge should be further examined if the bleeding persists for more than one week to exclude papillomas [7]. It is important to create awareness among the medical healthcare personnel regarding proper counseling and management of this benign condition, to avoid causing anxiety to the mothers and unnecessary investigations [7].
REFERENCES
1. Merlob P, Aloni R, Prager H, Mor N, Litwin A. Blood-stained maternal milk: prevalence, characteristics and counselling. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1990;35:153-7.


2. ├ćintesun E, Gul A, Akar S, Ezveci H, Celik C. Rusty pipe syndrome. Perinatoloji Dergisi 2017;25:85-6.

3. Deboni FA, Moldenhauer M, do-Nascimento MB. ŌĆ£Rusty pipeŌĆØ syndrome: benign and rare cause of bloody nipple discharge during breastfeeding: case report. Residencia Pediatrica 2018;8:151-3.

4. Gueye M, Kane-Gueye SM, Mbaye M, Ndiaye-Gueye MD, Faye-Dieme ME, Diouf AA, et al. Rusty pipe syndrome in a 22-year-old primigravida at 26 weeksŌĆÖ gestation. S Afr J Obstet Gynaecol 2013;19:17-8.

6. Mitchell KB, Johnson HM, Eglash A, Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine. ABM clinical protocol #30: breast masses, breast complaints, and diagnostic breast imaging in the lactating woman. Breastfeed Med 2019;14:208-14.


8. World Health Organization; United Nations ChildrenŌĆÖs Fund. Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative: revised, updated and expanded for integrated care: session 12: breast and nipple conditions [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009 [cited 2020 Jan 20]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK153471/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK153471.pdf
9. Li A, Kirk L. Intraductal papilloma [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 [cited 2020 Jan 20]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519539/