|
 |
- Search
| Korean J Fam Med > Volume 42(3); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
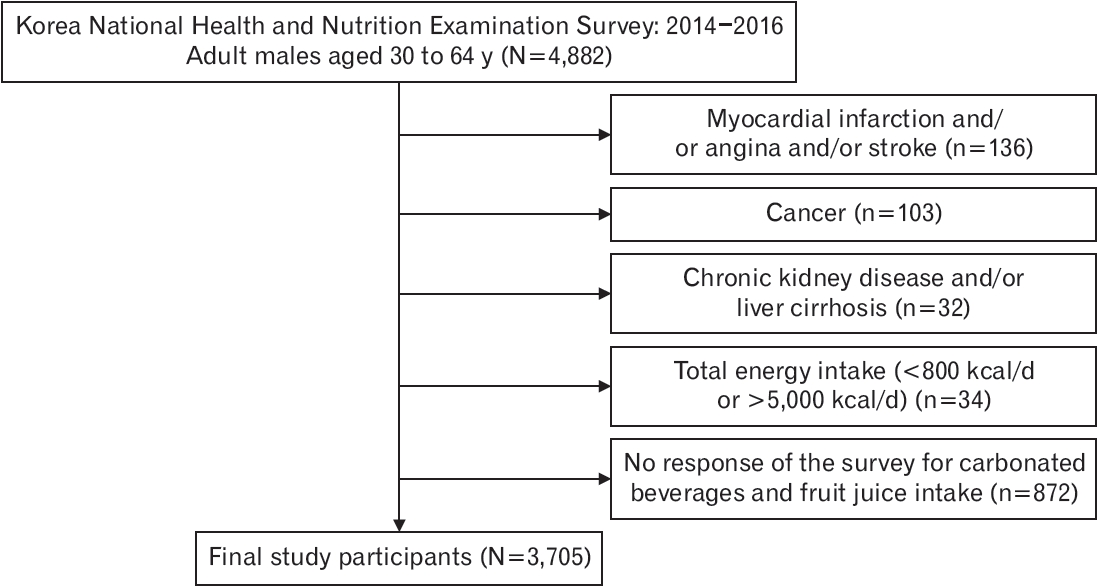
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Table┬Ā1.
| Characteristic |
Consumption of SSB (times/wk) |
P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ōēż2 | 3ŌĆō4 | Ōēź5 | Total | |||
| No. of participants | 2,440 (65.7) | 410 (11.1) | 239 (6.5) | 3,705 | ||
| Age (y) | 46.5┬▒0.3 | 40.8┬▒0.4 | 40┬▒0.6 | 45.5┬▒0.2 | <0.01 | |
| Married | 1,984 (86.9) | 342 (82.8) | 410 (75.1) | 2,914 (85.4) | <0.01 | |
| Education | ||||||
| ŌĆā | Elementary school or less | 129 (5.7) | 13 (3.1) | 9 (3.7) | 200 (5.9) | <0.01 |
| Middle school | 158 (6.9) | 21 (5.1) | 7 (2.8) | 231 (6.8) | ||
| High school | 667 (29.2) | 101 (24.5) | 61 (25.9) | 983 (28.8) | ||
| College or more | 1,123 (49.2) | 231 (55.8) | 132 (55.6) | 1,651 (48.4) | ||
| Employed | 1,877 (82.2) | 335 (81.1) | 192 (91.0) | 2,759 (80.9) | <0.01 | |
| Household income | ||||||
| Low | 147 (6.5) | 15 (3.7) | 12 (4.9) | 241 (7.0) | <0.01 | |
| Middle-low | 501 (22.0) | 89 (21.4) | 51 (21.6) | 766 (22.5) | ||
| Middle-high | 741 (32.5) | 148 (35.9) | 89 (37.4) | 1,097 (32.2) | ||
| High | 883 (38.7) | 161 (38.9) | 86 (36.1) | 1,292 (37.9) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.8┬▒0.1 | 24.6┬▒0.2 | 25.2┬▒0.3 | 24.8┬▒0.1 | 0.21 | |
| Smoking | ||||||
| Never smoker | 532 (23.3) | 94 (22.7) | 47 (19.9) | 757 (22.2) | <0.01 | |
| Ex-smoker | 754 (33.1) | 121 (29.2) | 62 (26.1) | 1,081 (31.7) | ||
| Current smoker | 987 (39.3) | 179 (43.5) | 115 (48.4) | 1,415 (41.5) | ||
| Alcohol use* | 1,673 (73.3) | 302 (73.1) | 178 (74.7) | 2,495 (73.2) | <0.01 | |
| Regular PAŌĆĀ | 1,110 (48.6) | 196 (47.4) | 119 (49.9) | 1,620 (47.5) | <0.01 | |
| HypertensionŌĆĪ | 329 (14.4) | 37 (9.0) | 12 (5.1) | 469 (13.7) | <0.01 | |
| Diabetes mellitusŌĆĪ | 140 (6.1) | 13 (3.2) | 3 (1.0) | 188 (5.5) | <0.01 | |
| DyslipidemiaŌĆĪ | 253 (11.1) | 35 (8.4) | 19 (8.1) | 354 (10.4) | <0.01 | |
| Stressed┬¦ | 585 (25.7) | 123 (29.6) | 91 (38.2) | 934 (27.4) | <0.01 | |
| Total energy intake (kcal/d) | 2,191┬▒17.0 | 2,516┬▒41.6 | 2,785┬▒63.9 | 2,285┬▒15.9 | <0.01 | |
| Carbohydrate intake (g/d) | 333┬▒2.9 | 373┬▒5.7 | 411┬▒9.0 | 346┬▒2.1 | <0.01 | |
| Protein intake (g/d) | 69┬▒0.7 | 83┬▒1.7 | 92┬▒3.0 | 73┬▒0.7 | <0.01 | |
| Total fat intake (g/d) | 41┬▒0.6 | 54┬▒1.3 | 61┬▒2.2 | 44┬▒0.5 | <0.01 | |
Values are presented as number (%) or mean┬▒standard error. P-values were calculated using the chi-square test or one-way analysis of variance. P<0.05 indicate statistical significance.
SSBs, sugar-sweetened beverages; PA, physical activity.
* Alcohol use is defined as consumption of one or more glasses of alcohol per month in the past year.
ŌĆĀ Regular PA was defined as Ōēź2.5 hours of moderate-intensity PA, Ōēź1.25 hours of high-intensity PA, or a combination of both (1 minute of high-intensity activity is equivalent to 2 minutes of moderate-intensity activity) per week.
Table┬Ā2.
Values are presented as odds ratio (95% confidence interval). High CVD risk is defined as has a 10-year CVD risk Ōēź10%. ORs and P trends were estimated using multivariateadjusted logistic regression analysis. Model 1: adjusted for age; model 2: adjusted for model 1 plus marital status, education, employment, household income, body mass index, alcohol use, regular physical activity, dyslipidemia, and stress; and model 3: adjusted for model 2 plus carbohydrate intake (g/d), protein intake (g/d), and total fat intake (g/d).
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; SSBs, sugar-sweetened beverages.
Table┬Ā3.
| Variable |
Consumption of SSB (times/wk) |
P trend | P for interaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ōēż2 | 3ŌĆō4 | Ōēź5 | |||
| Age (y) | 0.21 | ||||
| ŌĆā<45 | 1.00 | 0.90 (0.47ŌĆō1.75) | 2.39 (1.17ŌĆō4.88) | <0.05 | |
| ŌĆāŌēź45 | 1.00 | 1.31 (0.82ŌĆō2.10) | 0.78 (0.39ŌĆō1.56) | 0.93 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.18 | ||||
| ŌĆā<25 | 1.00 | 1.43 (0.84ŌĆō2.46) | 1.33 (0.47ŌĆō3.77) | 0.34 | |
| ŌĆāŌēź25 | 1.00 | 1.45 (0.86ŌĆō2.43) | 1.84 (0.94ŌĆō3.61) | 0.04 | |
| Regular PA* | |||||
| ŌĆāYes | 1.00 | 1.45 (0.84ŌĆō2.52) | 1.29 (0.60ŌĆō2.78) | 0.27 | 0.01 |
| ŌĆāNo | 1.00 | 1.60 (0.99ŌĆō2.60) | 2.35 (1.08ŌĆō5.10) | 0.01 | |
| Total energy intake (kcal/d) | |||||
| ŌĆā<2,400 | 1.00 | 1.48 (0.87ŌĆō2.51) | 1.25 (0.54ŌĆō2.90) | 0.26 | 0.23 |
| ŌĆāŌēź2,400 | 1.00 | 1.59 (0.95ŌĆō2.68) | 2.01 (1.01ŌĆō4.00) | 0.02 | |
| Carbohydrate intake (g/d) | |||||
| ŌĆā<350 | 1.00 | 1.63 (0.95ŌĆō2.78) | 1.37 (0.58ŌĆō3.24) | 0.16 | 0.06 |
| ŌĆāŌēź350 | 1.00 | 1.33 (0.81ŌĆō2.19) | 1.66 (0.83ŌĆō3.31) | 0.10 | |
Values are presented as odds ratio (95% confidence interval). High CVD risk is defined as has a 10-year CVD risk Ōēź10%. ORs and P trends for age in subgroup were estimated using multivariate logistic regression analysis after adjusting for marital status, education, employment, household income, BMI, alcohol use, regular PA, dyslipidemia, stress, carbohydrate intake (g/d), protein intake (g/d), and total fat intake (g/d). ORs and P trends for BMI in subgroup were estimated using multivariate logistic regression analysis after adjusting for age marital status, education, employment, household income, alcohol use, regular PA, dyslipidemia, stress, carbohydrate intake (g/d), protein intake (g/d), and total fat intake (g/d). ORs and P trends for regular PA in subgroup were estimated using multivariate logistic regression analysis after adjusting for age marital status, education, employment, household income, BMI, alcohol use, dyslipidemia, stress, carbohydrate intake (g/d), protein intake (g/d), and total fat intake (g/d). ORs and P trends for total energy intake in subgroup were estimated using multivariate logistic regression analysis after adjusting for age marital status, education, employment, household income, BMI, alcohol use, regular PA, dyslipidemia, stress, carbohydrate intake (g/d), protein intake (g/d), and total fat intake (g/d). ORs and P trends for carbohydrate intake in subgroup were estimated using multivariate logistic regression analysis after adjusting for age marital status, education, employment, household income, BMI, alcohol use, regular PA, dyslipidemia, stress, protein intake (g/d), and total fat intake (g/d).
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; SSBs, sugar-sweetened beverages; BMI, body mass index; PA, physical activity.
REFERENCES
- TOOLS