|
 |
- Search
| Korean J Fam Med > Volume 38(4); 2017 > Article |
Abstract
Background
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are toxic materials that cannot be broken down naturally and that easily accumulate in the body. Although several studies have attempted to uncover the effects of POPs on the endocrine and nervous systems and on cancer, few focus on the relationship between low-dose POPs and public health. Here, we attempt to determine the relationship between the level of POPs and common gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and constipation.
Methods
We recruited 121 subjects who visited Kyungpook National University Medical Center for health screening. Plasma concentrations were evaluated for 40 kinds of POPs including 17 types of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and 23 types of organochlorine pesticides (OCP). Furthermore, the Korean version of the Rome III criteria was used to identify gastrointestinal symptoms.
Results
Based on our results, abdominal discomfort showed an inverse relationship with several PCBs and an inverted U-shaped relationship with several other OCPs including pp-DDD and pp-DDT. The effects of pp-DDD and pp-DDT on abdominal discomfort were similar to those of OCPs on obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are toxic chemicals that accumulate in animals and plants through the food chain, and they do not decompose in the environment through photochemical, biological, and chemical processes. The most common types of POPs are polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs). PCBs have been used frequently in electric equipment, dielectric coolants, dielectric fluids, paints, and coating materials for over five decades. In particular, the primary use of the chemicals was as sealants in the doors and windows of buildings constructed from the 1950s to the 1970s. PCBs have been detected at high concentrations in the indoor air of these buildings several decades after construction.1,2,3,4) OCPs are commonly used worldwide because of their low cost and outstanding insecticidal activity.5) However, POPs are highly toxic substances characterized by high residual properties, bioconcentration potential, and long-distance mobility. Responsive measures have been devised around the globe because of the increased incidence of damage to ecosystems and human health. A total of 21 POPs were listed in the Stockholm Convention on POPs that required regulations in 2004 and 2009. Restrictions on the use of POPs since the early 1970s have slowly reduced the environmental load of POP compounds in a large number of places worldwide.6) Despite these efforts, a recent study showed that workers in a transformer recycling company and their family members had highly elevated levels of PCBs in their blood7) and the association of POPs with various diseases is still being reported because of the unique properties of POPs, requiring consistent monitoring.
Previous studies mainly investigated the high concentrations of POPs and proposed an association with a wide range of symptoms8,9) including acneiform eruption, dermal pigmentation, and increased eye discharge. Recent studies have analyzed the effects of low levels of POPs and reported that POPs at low concentrations are associated with estrogenic activity,10) diabetes mellitus,11,12,13) endocrine diseases such as obesity,14,15) brain and psychomotor development,16) and cancer.17) However, almost no studies have investigated the association of the intake of POPs from food with gastric problems in humans.18,19,20)
Abdominal discomfort is one of the most common digestive symptoms these days. A study reported that a statistically significant decrease was observed in the quality of life as the severity of abdominal discomfort increased.18) Another study demonstrated that various types of abdominal complaints are associated with depression and anxiety.21) Because abdominal discomfort is a subjective symptom and the exact cause has not been clarified, evaluation of the various causes is crucial. A previous study suggested that a low level of PCBs in the body is a possible cause of abdominal discomfort.22) However, this study mainly analyzed the difference in the symptoms of groups classified according to the history of exposure to PCBs, and did not clearly state the relationship of the subjective symptoms with different concentrations of PCBs. For these reasons, the aim of this study was to analyze the association of POP concentrations with various gastrointestinal symptoms including abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and constipation from multiple perspectives.
This study included 121 healthy subjects who visited Kyungpook National University Medical Center for health screening from March to July, 2012. Subjects who had no previous psychiatric disorders or severe chronic conditions, such as cancer, were included in the study, and all subjects provided written informed consent. According to a study on the correlation of POP concentrations with the onset of obesity,15) the body mass index (BMI) of subjects were taken into consideration during the recruitment process. Fifty-one subjects with BMI >25.0 kg/m2 were included in the study. All subjects were asked to complete the survey questionnaire. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Kyungpook National University Medical Center (KNUH 2012-02-018).
Weight, height, waist, hip, and thigh circumferences, the thickness of subcutaneous fat at the triceps muscles, blood pressure, and pulse were measured. Using the measured values, BMI (kg/m2) was calculated.
Smoking status was divided into non-smoker, former smoker, and current smoker. Drinking status was divided into non-drinker, former drinker, and current drinker. Drinkers were asked about their average frequency of alcohol consumption and the mean dose of alcohol consumed per drinking session in the past year prior to their visit.
The presence of symptoms including gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal discomfort were evaluated with the Korean version of the Rome III (Rome III-K) criteria for the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The Rome III-K is the translated version23) of the Rome III criteria24) published by the Korean Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility in 2006. The Rome III criteria, with a sensitivity of 80.3% and specificity of 50.0%, are relatively useful in diagnosing functional bowel disorders in Koreans.
This study examined 17 types of PCBs, namely PCB74, PCB99, PCB105, PCB118, PCB138, PCB146, PCB153, PCB156, PCB157, PCB164, PCB167, PCB172, PCB177, PCB178, PCB180, PCB183, and PCB187 and 23 types of OCPs including hexachlorobenzene (HCBz), ╬▒-HCH, ╬▓-HCH, ╬│-HCH (Lindane), ╬┤-HCH, cis-/trans-nonachlor, heptachlor, cis-/trans-heptachlor epoxide, cis-/trans-chlordane, oxychlordane, aldrin, dieldrin, endrin, mirex, 4,4'-DDT, 4,4'-DDE, 4,4'-DDD, 2,4'-DDT, 2,4'-DDE, and 2,4'-DDD. The samples were preprocessed through clean-up with a Silica-Florisil cartridge and HLB cartridge, using solid phase extraction. For instrumental analyses, we used high resolution gas chromatography and mass spectrometry with high resolution tandem MS spectrometry (JMS-800 T; JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
The levels of POPs were categorized into five groups using quintiles to identify the association of POP concentrations with the onset of symptoms. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the association of the quintiles of plasma POPs with gastrointestinal symptoms including abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and constipation. We also conducted additional analysis using IBS diagnosis as a dependent variable. Chi-square test for trends was used to evaluate linear patterns for the effects of POP levels on abdominal symptoms. We used the statistical software IBM SPSS for Windows ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and considered a P-value <0.05 as statistically significant; however, considering the small sample size, we also commented on results with 0.05 Ōēż P-value <0.1 as marginally significant.
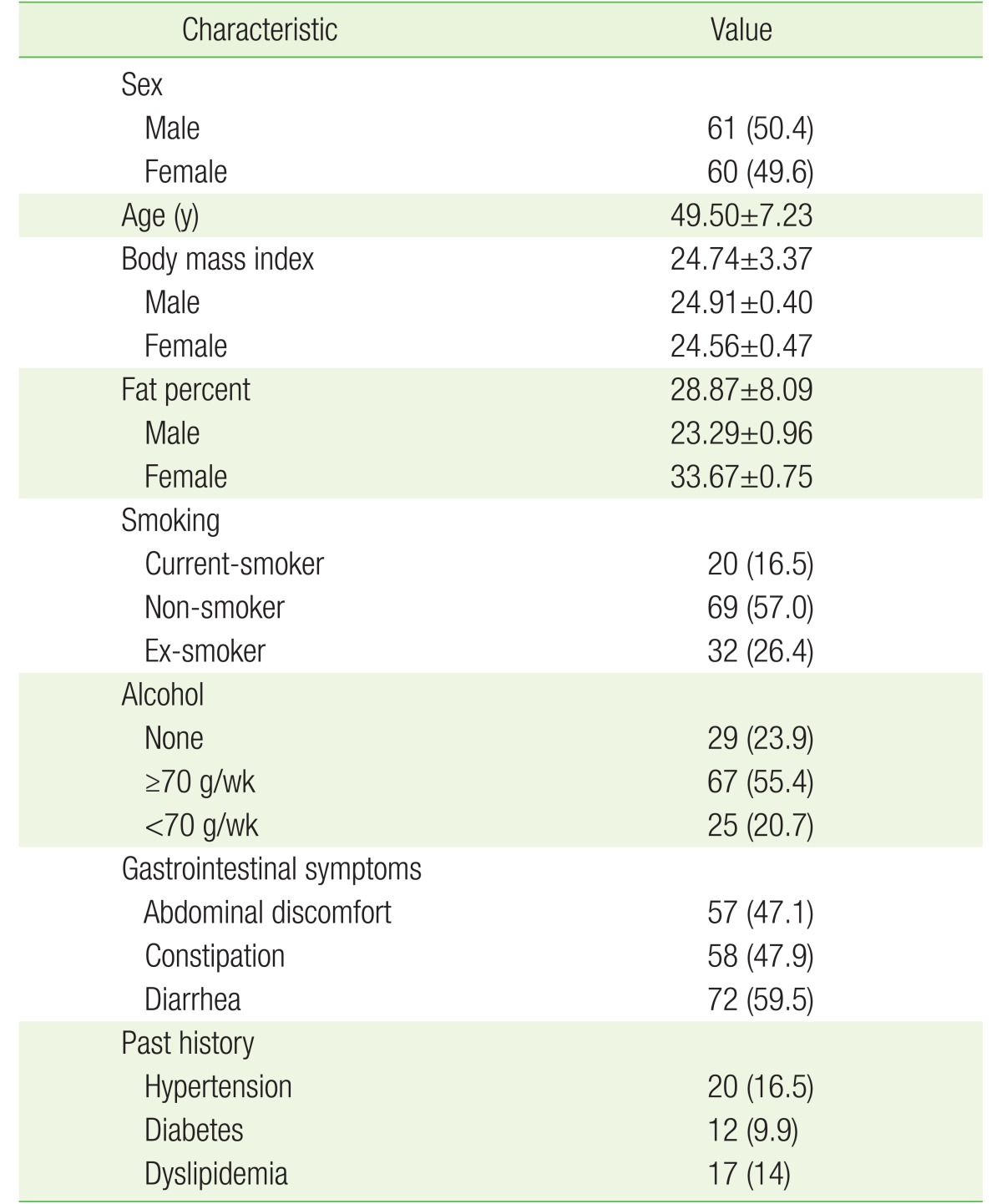
The subjects consisted of 61 men and 60 women with a mean age of 49.5 years (range, 38 to 66 years). Sixty-nine subjects were current smokers, and the others were non-smokers (N=20) or former smokers (N=32). Ninety-two subjects were alcohol drinkers: 25 subjects consumed less than 70 g/wk and the others consumed 70 g/wk or more. The mean┬▒standard deviation BMI score was 24.74┬▒3.37. The number of subjects that reported constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort was 58, 72, and 57, respectively. Detailed information on the general characteristics is provided in Table 1.
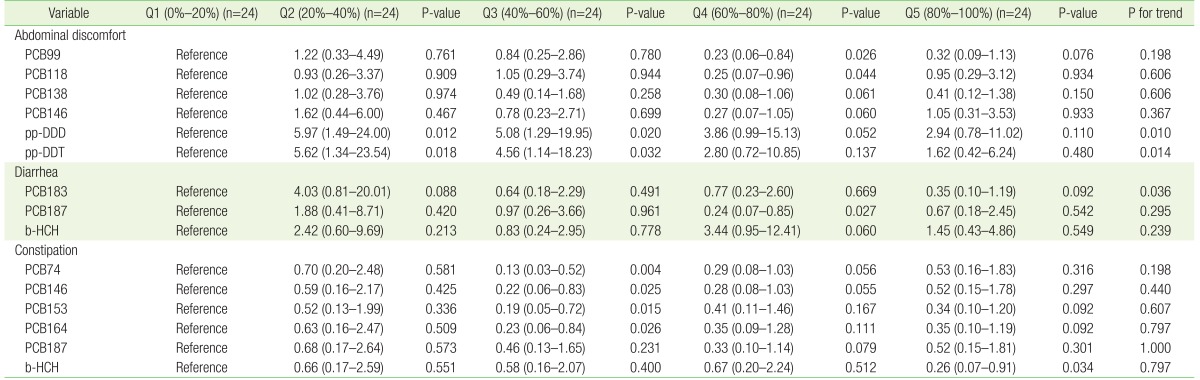
Subjects were divided into five groups based on the quintiles of plasma concentrations of POPs, and the odds ratios for every quintile were obtained for each symptom. Logistic regression analysis adjusting for age, sex, smoking, alcohol and BMI15) was performed to identify the correlation between the POPs and the severity of the abdominal symptoms. Table 2 presents the results with statistical significance.
A number of POPs showed statistical significance with gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and constipation. In the case of abdominal discomfort, the odd ratios of the 4th quintile decreased to 0.23ŌĆō0.30, compared with those of the 1st quintile of PCBs. Statistical significance was observed for PCB99 and PCB118 (P<0.05), indicating an inverse association. In contrast, the odd ratios of the 2nd and 3rd quintiles increased to about 5 on average, compared with those of the 1st quintile for OCPs including pp-DDD and pp-DDT (P<0.05), and then showed a gradually decreasing tendency, indicating an inverted U-shaped association. A P for trend of 0.01 was considered statistically significant. The resulting graph represents the odds ratios for the quintiles of the plasma concentrations of POPs that cause abdominal discomfort (Figure 1).
In the case of diarrhea, the odds ratios of the 2nd quintile were greater than those of the 1st quintile for PCB183 (P<0.05), and a gradually decreasing tendency was observed in the odd ratios of the 4th and 5th quintiles. PCB183 had statistical significance with a P for trend of 0.04, indicating an inverted U-shaped association.
In the case of constipation, the plasma concentrations of several PCBs were inversely associated with gastrointestinal symptoms. The odds ratios of PCBs (PCB74, PCB146, PCB153, and PCB164) that caused constipation decreased to 0.13ŌĆō0.23 in the 3rd quintile compared to the 1st quintile (all Ps<0.05), and were maintained between approximately 0.3ŌĆō0.5 in the 4th and 5th quintiles. The odds ratios of b-HCH (OCPs), which caused constipation, decreased to 0.6 on average in the 2nd-4th quintiles compared to the 1st quintile, and were maintained for a while. Moreover, the odds ratios decreased to 0.26 in the 5th quintile, with statistical significance.
However, in subsequent analysis using the diagnosis of IBS as a dependent variable, there was no significant association between the levels of POPs and the frequency of IBS diagnosis (all Ps>0.05).
Gastrointestinal symptoms including abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and constipation were found to be statistically significantly correlated with a number of POPs examined in this study. Abdominal discomfort had an inverted U-shaped association with OCPs including pp-DDD and pp-DDT. This association is similar to the association identified between POPs and obesity as well as metabolic syndrome in previous investigations.14,15,25) Even though BMI was modified to reduce the effects of obesity and metabolic syndrome, similar association patterns for POPs were observed with other diseases including obesity. Based on these previous results, the plasma concentrations of some POPs were anticipated to be associated with abdominal discomfort.
In a previous study on the relationship between the degree of exposure to POPs and gastric complaints, no significant difference was found in subjects working in buildings exposed to POPs when the severity of gastric complaints was compared with that of the control group.22) Although the number of POPs included in this study is small,22) the outcomes are predicted to be drawn from the non-linear association proposed in a previous study with subjects under low-dose exposure to POPs.
This investigation provides stronger evidence than previous studies by comparing the plasma concentrations of various POPs with the severity of abdominal discomfort. For abdominal discomfort, greater odds ratios for OCPs were found in lower plasma concentrations (quintile 2 and quintile 4) than in higher plasma concentrations (quintile 4 and quintile 5). Taking into consideration the fact that gastrointestinal symptoms can influence the absorption of substances into the body, the outcome could be interpreted with reverse causality. Thus, higher absorption could be attributed to a higher concentration of POPs in an asymptotic case with abdominal discomfort, while lower absorption could be attributed to a lower concentration of POPs because of reduced gastrointestinal function. Lower POP levels are believed to be due to limited gastrointestinal absorption with constant abdominal discomfort. Therefore, the association with plasma POP concentrations should be considered in cases of mild abdominal discomfort with unknown causes.
This study has several limitations. The sample size was relatively small, and subjects were recruited from one general hospital. Therefore, our results cannot be generalized beyond the study samples. Additional studies with a larger sample group are crucial to further investigate the associations of plasma concentrations of POPs with subdivided symptoms. In addition, our cross-sectional design cannot confirm causality between abdominal symptoms and POP levels.
Although there are some limitations, this study has the following merits. Functional gastrointestinal disease including IBS is one of the leading disorders associated with abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and constipation. The exact cause of this common gastrointestinal disease has not yet been clarified. So far, functional gastrointestinal disorders are known to mainly occur due to individual factors including stress,26) food,27) individual lifestyle habits, and body constitution from a clinical perspective. In addition, this study suggests that these common gastrointestinal symptoms can be associated with environmental factors such as POPs, in addition to individual factors. The findings of this study are anticipated to contribute to the creation of a healthier environment through policy change that prohibits the use of environmental pollutants. Moreover, this study suggests that an appropriate approach for diseases from a social perspective be taken beyond the individual symptom-oriented diagnostic approach.
In conclusion, some POPs had a statistically significant association with gastrointestinal symptoms including abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and constipation. OCPs had an inverted U-shaped relationship, similar to the results of previous studies. Therefore, the concentrations of POPs should be considered when determining the association of gastrointestinal symptoms with unknown causes such as mild abdominal discomfort. Our results indicate that clinicians should be concerned with environmental issues including the use of POPs, which is closely linked to public health.
References
1. Balfanz E, Fuchs J, Kieper H. Sampling and analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in indoor air due to permanently elastic sealants. Chemosphere 1993;26:871-880.

2. Fromme H, Baldauf AM, Klautke O, Piloty M, Bohrer L. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in caulking compounds of buildings: assessment of current status in Berlin and new indoor air sources. Gesundheitswesen 1996;58:666-672. PMID: 9081511.

3. Herrick RF, McClean MD, Meeker JD, Baxter LK, Weymouth GA. An unrecognized source of PCB contamination in schools and other buildings. Environ Health Perspect 2004;112:1051-1053. PMID: 15238275.



4. Priha E, Hellman S, Sorvari J. PCB contamination from polysulphide sealants in residential areas-exposure and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2005;59:537-543. PMID: 15788176.


5. Voldner EC, Li YF. Global usage of selected persistent organochlorines. Sci Total Environ 1995;160:201-210.

6. Sanders G, Eisenreich SJ, Jones KC. The rise and fall of PCBs: timetrend data from temperateindustrialised countries. Chemosphere 1994;29:2201-2208.

7. Schettgen T, Gube M, Esser A, Alt A, Kraus T. Plasma polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) levels of workers in a transformer recycling company, their family members, and employees of surrounding companies. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2012;75:414-422. PMID: 22686300.


8. Yu ML, Guo YL, Hsu CC, Rogan WJ. Menstruation and reproduction in women with polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) poisoning: long-term follow-up interviews of the women from the Taiwan Yucheng cohort. Int J Epidemiol 2000;29:672-677. PMID: 10922344.


9. Masuda Y. Fate of PCDF/PCB congeners and change of clinical symptoms in patients with Yusho PCB poisoning for 30 years. Chemosphere 2001;43:925-930. PMID: 11372885.


10. Welshons WV, Thayer KA, Judy BM, Taylor JA, Curran EM, vom Saal FS. Large effects from small exposures: I. Mechanisms for endocrinedisrupting chemicals with estrogenic activity. Environ Health Perspect 2003;111:994-1006. PMID: 12826473.



11. Lee DH, Lee IK, Song K, Steffes M, Toscano W, Baker BA, et al. A strong dose-response relation between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and diabetes: results from the National Health and Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1638-1644. PMID: 16801591.


12. Lee DH, Lee IK, Jin SH, Steffes M, Jacobs DR Jr. Association between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and insulin resistance among nondiabetic adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetes Care 2007;30:622-628. PMID: 17327331.


13. Lee DH, Steffes MW, Sjodin A, Jones RS, Needham LL, Jacobs DR Jr. Low dose of some persistent organic pollutants predicts type 2 diabetes: a nested case-control study. Environ Health Perspect 2010;118:1235-1242. PMID: 20444671.



14. Lee DH, Steffes MW, Sjodin A, Jones RS, Needham LL, Jacobs DR Jr. Low dose organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls predict obesity, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance among people free of diabetes. PLoS One 2011;6:e15977PMID: 21298090.



15. Lee DH, Lind L, Jacobs DR Jr, Salihovic S, van Bavel B, Lind PM. Associations of persistent organic pollutants with abdominal obesity in the elderly: the Prospective Investigation of the Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors (PIVUS) study. Environ Int 2012;40:170-178. PMID: 21835469.


16. Gascon M, Verner MA, Guxens M, Grimalt JO, Forns J, Ibarluzea J, et al. Evaluating the neurotoxic effects of lactational exposure to persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in Spanish children. Neurotoxicology 2013;34:9-15. PMID: 23085522.


17. Prince MM, Ruder AM, Hein MJ, Waters MA, Whelan EA, Nilsen N, et al. Mortality and exposure response among 14,458 electrical capacitor manufacturing workers exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Environ Health Perspect 2006;114:1508-1514. PMID: 17035134.



18. Fisk AT, Hobson KA, Norstrom RJ. Influence of chemical and biological factors on trophic transfer of persistent organic pollutants in the northwater polynya marine food web. Environ Sci Technol 2001;35:732-738. PMID: 11349285.


19. Jacobs MN, Covaci A, Schepens P. Investigation of selected persistent organic pollutants in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), salmon aquaculture feed, and fish oil components of the feed. Environ Sci Technol 2002;36:2797-2805. PMID: 12144249.


20. Kelly BC, Ikonomou MG, Blair JD, Morin AE, Gobas FA. Food webspecific biomagnification of persistent organic pollutants. Science 2007;317:236-239. PMID: 17626882.


21. Bouchoucha M, Hejnar M, Devroede G, Babba T, Bon C, Benamouzig R. Anxiety and depression as markers of multiplicity of sites of functional gastrointestinal disorders: a gender issue? Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 2013;37:422-430. PMID: 23270854.


22. Broding HC, Schettgen T, Hillert A, Angerer J, Goen T, Drexler H. Subjective complaints in persons under chronic low-dose exposure to lower polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Int J Hyg Environ Health 2008;211:648-657. PMID: 18396099.


23. Kim ES, Lee BJ, Kim YS, Lee SI, Park H. Validation of Rome III criteria in the diagnosis of functional gastrointestinal disorders in Korean patients. Korean J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2008;14:39-44.
24. Drossman DA. The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. Gastroenterology 2006;130:1377-1390. PMID: 16678553.


25. Lee DH, Lee IK, Porta M, Steffes M, Jacobs DR Jr. Relationship between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome among non-diabetic adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetologia 2007;50:1841-1851. PMID: 17624515.


26. Posserud I, Agerforz P, Ekman R, Bjornsson ES, Abrahamsson H, Simren M. Altered visceral perceptual and neuroendocrine response in patients with irritable bowel syndrome during mental stress. Gut 2004;53:1102-1108. PMID: 15247175.



27. Atkinson W, Sheldon TA, Shaath N, Whorwell PJ. Food elimination based on IgG antibodies in irritable bowel syndrome: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 2004;53:1459-1464. PMID: 15361495.



Figure┬Ā1
Effects of several persistent organic pollutants on abdominal discomfort. Although none of the PCBs showed any significant trends (A-D), pp-DDD and pp-DDT have a significant inverted U-shaped relationship (E, F). (A) PCB99; (B) PCB118; (C) PCB138; (D) PCB146; (E) pp-DDD; (F) pp-DDT. In pp-DDD and pp-DDT analysis, groups Q2 and Q3 reported higher abdominal discomforts than group Q1. Reference group is Q1 in the analysis. PCB, polychlorinated biphenyl. *P<0.05. ŌĆĀP<0.1.

- TOOLS